Individual income tax can be overwhelming and complex for many people. With the ever-changing tax laws and regulations, it’s important to stay informed and understand how it impacts your financial situation. In this blog post, we will dive into the world of individual income tax, whether you’re a first-time taxpayer or looking for ways to optimize your tax deductions, this blog will serve as your comprehensive guide to understanding and managing individual income tax.
What is individual income tax?
It is a form of taxation imposed on the income earned by individuals. It is one of the primary sources of revenue for the government and plays a critical role in funding various public services, such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure development. The concept behind it is rooted in the principle of equity, where individuals with higher incomes are required to contribute a proportionally higher amount compared to those with lower incomes.
Its progressive nature means that as your income increases, so does the percentage you pay in taxes. This creates a sense of fairness among taxpayers, as those who can afford more financially shoulder a greater burden. However, this system has its critics who argue that high-income earners should not be disproportionately taxed.
Income Tax Rates
For Individual Citizens and Resident Aliens Earning Purely Compensation Income and Individuals Engaged in Business and Practice of Profession
A. Graduated Income Tax Rates under Section 24(A)(2) of the Tax Code of 1997, as amended by Republic Act No. 10963

B. For Purely Self-Employed Individuals and/or Professionals Whose Gross Sales/Receipts and Other Non-Operating Income Do Not Exceed the VAT Threshold of P3,000,000, the tax shall be, at the taxpayer’s option:
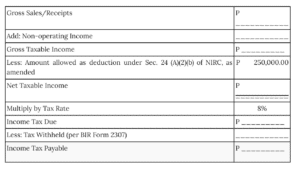
- 8% on Gross Sales or Gross Receipts in Excess of P250,000 in Lieu of the Graduated Income Tax Rates and the Percentage Tax; Or
- Income Tax Based on the Graduated Income Tax Rate.
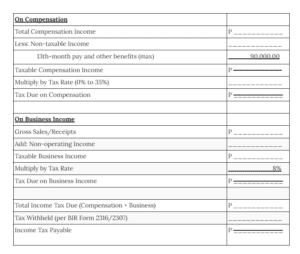
C. For Individuals Earning Both Compensation Income and Income from Business and/or Practice of Profession, their income taxes shall be:
- For Income from Compensation: Based on Graduated Income Tax Rates; and
- For Income from Business and/or Practice of Profession:
If the total Gross Sales/Receipts Do Not Exceed VAT Threshold of P3,000,000, the Individual Taxpayer May Opt to Avail:
- 8% Income Tax on Gross Sales/Receipts and Other Non-Operating Income in Lieu of the Graduated Income Tax Rates and the Percentage Tax; Or
- Income Tax Based on Graduated Income Tax Rates
- If the total Gross Sales/Receipts Exceed VAT Threshold of P3,000,000
- Income Tax Based on Graduated Income Tax Rates
How is Income Tax payable of individuals (resident citizens and non-resident citizens) computed?
- Based on Graduated Income Tax Rate Based on Preferential Tax Rate of 8%

- Taxpayers source of income is purely from self-employment
- Mixed Income Earner
It serves a crucial purpose in funding government programs and services that benefit society as a whole. It ensures that citizens contribute their fair share based on their earnings, promoting a sense of equity and social responsibility. The revenue generated from it is used to support various sectors such as education, healthcare, infrastructure, and defense.
Additionally, it helps in wealth redistribution by reducing income inequalities and providing assistance to low-income individuals through refundable tax credits. While the complexities and debates surrounding individual income tax are ongoing, its importance in maintaining the functioning of our society cannot be undermined. It is essential for individuals to understand their tax obligations and actively participate in shaping tax policies to ensure fairness and efficiency in the system.
For more insights on tax planning and optimization, don’t miss our previous blog post.
Do you need assistance when it comes to Tax? Contact FilePino to give you guidance and assistance.
Landline: (02) 8478-5826
Mobile: 0917 892 2337
Email: info@filepino.com


